As email providers increase their spam protection measures, malicious senders figure out ways to get around them, so it’s unlikely that the problem will go away.
But there is some good news: AI spam filters offer new ways to protect inboxes from unwanted and potentially harmful content. I’ll take a look into how AI is helping to ensure your emails are delivered successfully.
Which Providers Use AI Filters?
Gmail has been using AI-assisted filtering since October 2023, as far as we know, and probably long before then! It says on its blog that it has “AI-powered defenses” against spam, phishing, and malware.
Microsoft says it also uses AI in Defender, which incorporates anti-malware and anti-phishing systems. This isn’t a surprise given that Microsoft has embedded AI tools into Windows.
Email security platforms like Barracuda are also using AI to analyze communication patterns within your organization and flag messages containing “suspicious and harmful content”.
What filters are these companies using and how are they fighting spam with AI?
How AI Spam Filters Work
AI spam filters typically rely on some form of machine learning. This means that the AI is trained to look for patterns and continually improve its understanding of spam.
Machine learning is a great way to get an algorithm to filter spam (and, conversely, avoid false positives – which can be equally annoying).
The AI spam filtering process looks something like this:
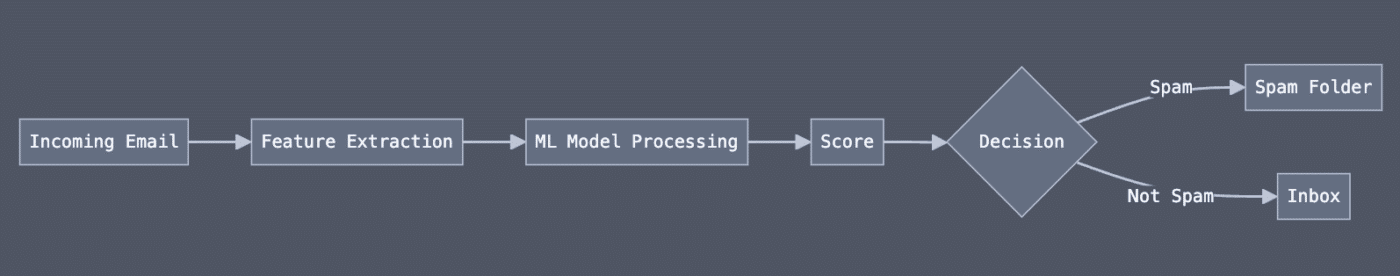
Here’s what’s happening at each stage.
- Incoming email: This is where the email is received by the server.
- Feature extraction: The email provider’s filter pulls out important information: the sender, the headers, the subject line, and even the links in the email body.
- ML model processing: This is where the AI kicks in. Using machine learning algorithms, the filter analyzes these features against its trained models and historical data. (I’ll explain a bit more about the algorithmic side of this in a second.)
- Score: Based on the analysis, the email receives a spam score based on the probability that it’s malicious or spam.
- Decision: Based on the score, the message is flagged as spam or allowed to continue to the mailbox.
ML Model Processing: Where the AI Magic Happens
Behind the ML Model Processing step, there’s a lot going on. Here’s that stage zoomed in so you can see it in more detail.
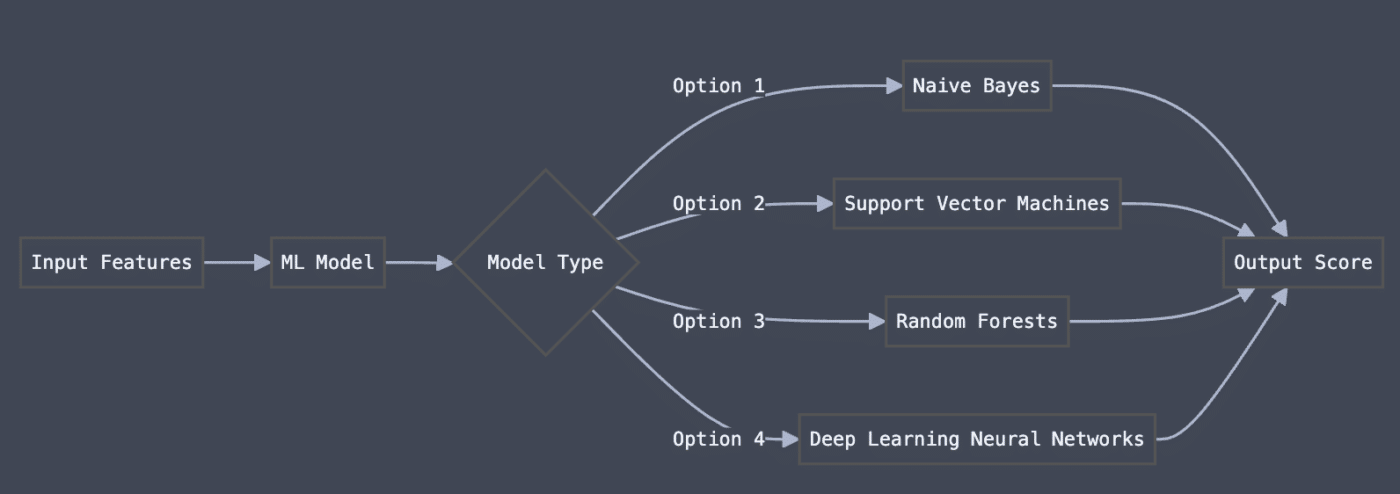
There’s a decision here: the ML Model Type. The anti-spam system has 4 options.
Naive Bayes
Naive Bayes is a used for simple, text-based emails. It can process large volumes at speed.
Here’s an example of how a search engine might use Bayes Theorem:
An internet search for “movie automatic shoe laces” brings up “Back to The Future”. Has the search engine watched the movie? No, but it knows from lots of other searches what people are probably looking for.
– Courtesy of Maths Is Fun
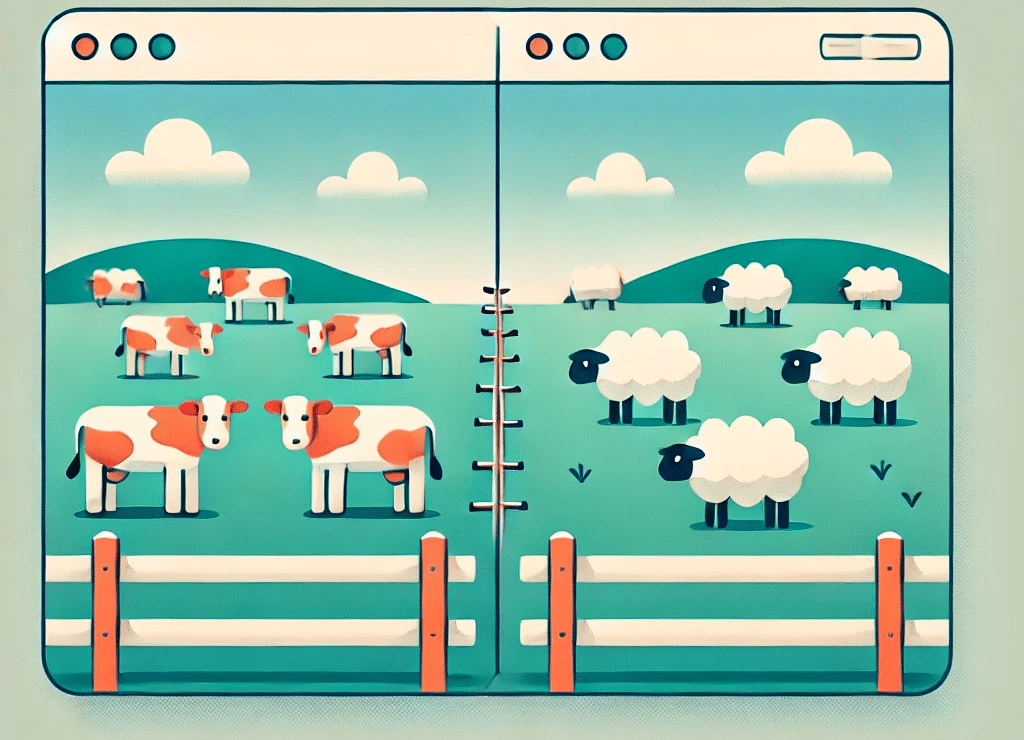
Support Vector Machines (SVM)
You can visualize SVM as follows: imagine two fields, one with cows, and one with sheep. The job of SVM is to create a fence that separates them, so it needs to figure out the characteristics of the cows (legitimate emails) and sheep (spam) so it can keep them apart.
This machine learning model is trained on very large amounts of data over a long period of time.
Random Forests
Random forests are a set of decision trees. The email is passed through the ‘forest’ of trees to see if it meets each criteria:
- Are there a ton of links in this email?
- Does the email have the word ‘free’ in it?
- What domain TLD is it from?
- How’s the grammar and spelling?
- Can I verify the sender? What does their past history look like?
- Does it have attachments?
- Is the sender on a blacklist?
Depending on the number of true/ false answers, the email might be marked as spam as it makes its way through the ‘forest’.
Deep Learning Neural Networks
The final algorithm is one you’ve likely heard of before. Neural networks are layered algorithms where each neuron makes one decision.
To detect spam, emails are filtered through the entire network, through every single layer. At the end, a yes/ no decision is made based on the outputs from the neurons.
Choosing an Algorithm
How does the AI spam filter choose one of these algorithms?
Each one is designed for a slightly different set of circumstances. Some are best for high volume text analysis. Some are more reliable than others. Some require much more processing power, or a provider might not have the time to train them.
In general, Naive Beyes is a good option for text-only emails, while more complex emails require a more complex algorithm.
Impact of AI Spam Filters on Email Deliverability
Now that we understand these models, we can start to see why the characteristics of our emails might trigger spam filters.
Improving the content and authentication could reduce your spam complaint rate by appearing more genuine to human users.
- In your marketing emails: AI filters mean we all need to pay attention to list hygiene and permission-based marketing. Sender reputation is a big deal!
- In your transactional emails: AI filters have improved delivery rates for legitimate transactional messages, but they’ve also heightened the importance of proper authentication and sending infrastructure. Maintaining consistent sending patterns and volumes is crucial, and so is having authentication.
- In your personal emails: AI filters offer better protection, so the emails you receive are less likely to be irritating or threatening. There’s always a small risk of occasional false positives for legitimate personal emails, as with all processes that are enhanced by AI.
To ensure your emails consistently reach the inbox, follow our 10 best practices:
- Authenticate your emails using SPF, DKIM, and DMARC protocols.
- Maintain a clean email list by regularly removing inactive subscribers.
- Personalize your content to match your audience’s interests and preferences.
- Optimize your email design with a balanced mix of text and images.
- Monitor your sender reputation using tools like Google Postmaster Tools.
- Be cautious with words and phrases commonly associated with spam.
- Encourage subscriber engagement through clear calls-to-action.
- Implement double opt-in for new subscribers to ensure list quality.
- Regularly test your emails against popular spam filters before sending.
- Maintain consistent sending patterns to avoid triggering spam filters.
By understanding how AI spam filters work and following best practices, you can significantly improve your email deliverability. Remember, the key is to send relevant, engaging content to recipients who have explicitly agreed to receive your messages.
Frequently Asked Questions About AI Spam Filters
Do AI spam filters read the content of my emails?
In a sense, yes they do.
AI spam filters analyze your emails automatically, including:
- Content: Words and phrases used
- Sender information: Email address and domain
- Email structure: Headers, attachments, links
- Sending patterns: Time, frequency, recipient list
Humans don’t read the emails in normal circumstances. There are just too many.
How often do AI spam filters update their algorithms?
Most filters have a feedback loop that allows them to learn continuously, although email providers and security services can apply their own updates.
Can AI spam filters be 100% accurate?
While highly effective, AI spam filters can’t achieve 100% accuracy. There’s always a small chance of false positives or false negatives.
Can using certain words guarantee my email will be marked as spam?
Modern AI filters consider context rather than relying solely on keyword matching. However, it’s still wise to avoid excessive use of words that are found in a high number of spam emails: ‘free’, ‘easy money’, ‘reverse aging’, ‘jackpot’, and ‘wire transfer’ are just a few examples.
That’s it! Now you know how how AI spam filters work
Next, would you like to learn how to get fewer spam complaints? Check out our tutorial on how to reduce your spam complaint rate for more information.