If you maintain an email list or you’re collecting users’ data via a form on your website, it’s your responsibility to make sure that data is kept safe and secure.
For businesses, protecting customer data is not just about following the law – it’s crucial for maintaining trust and ensuring your emails actually reach your audience.
Key regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and CAN-SPAM affect how businesses collect, store, and use customer information. Understanding and following these rules is essential for anybody using email marketing.
In this guide, I’ll explore what email data privacy means, why it matters for deliverability, and how you can protect your customers’ information while running effective email campaigns.
Understanding Email Data Privacy
As an email sender, whether you’re a company or an individual, it’s crucial to understand email data privacy. Proper handling of personal data keeps you on the right side of the law and builds trust with your recipients.
Personal data is any information that can identify an individual. When sending emails, you’re likely dealing with:
- Names
- Email addresses
- Physical addresses
- Phone numbers
- Dates of birth
- Purchase histories
- Interests and preferences
it’s crucial to understand that personal data can be highly sensitive. Not only do people want control over who knows what about them, but this data can also be used for malicious purposes such as phishing.

Treating all personal data as potentially sensitive is a good practice. This means implementing strong data protection measures, being transparent about data usage, and always respecting the privacy preferences of your recipients.
Whether you’re sending transactional emails to users on your website or marketing messages to your mailing list, you might collect data through newsletter sign-ups, online purchases, tracking pixels in emails, and website cookies
You may then use this data to personalize email content, segment your audience, improve your products or services, and analyze campaign performance.
Respecting the privacy of this valuable data is crucial because It builds trust with your audience and it can protect you from potential legal issues and fines
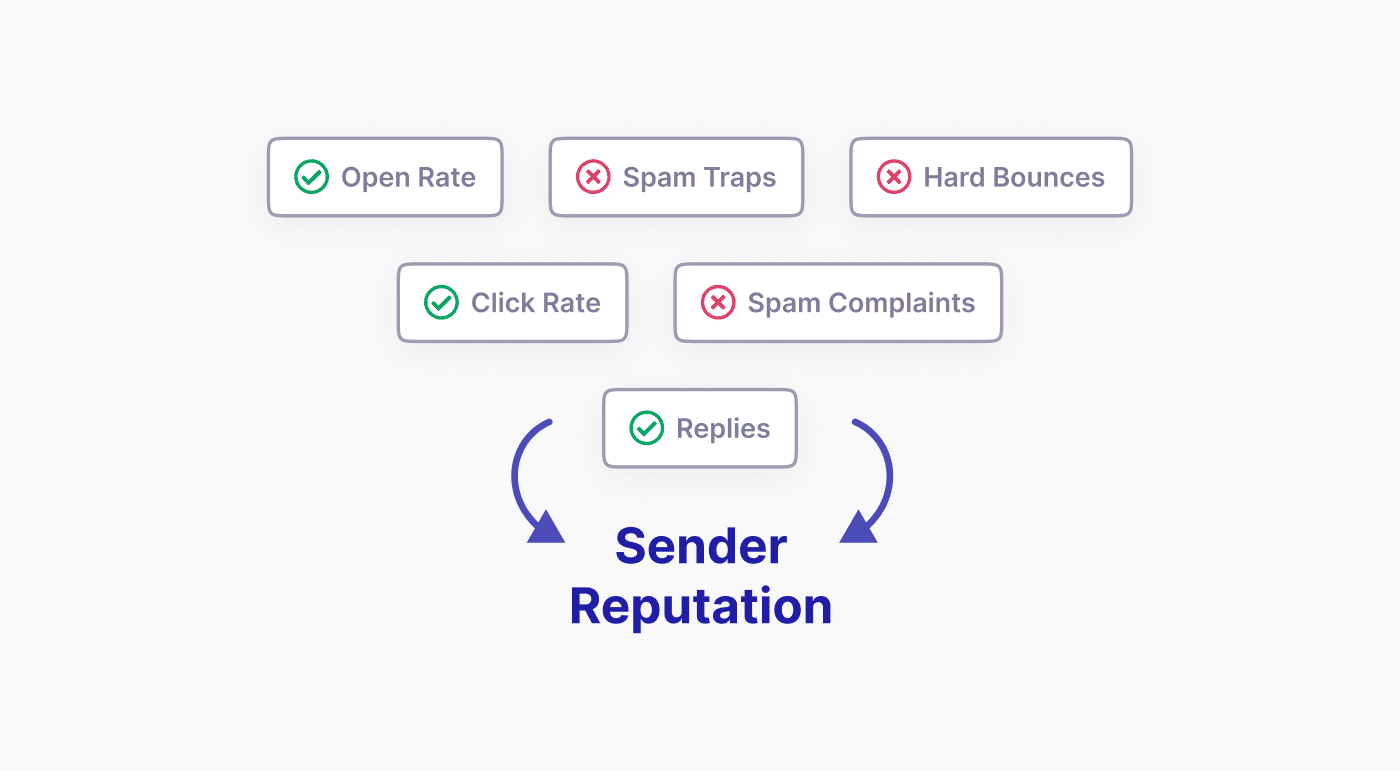
How Data Privacy Influences Sender Reputation and Deliverability
Maintaining strong data privacy practices doesn’t just keep you compliant with laws—it can significantly boost your sender reputation and email deliverability rates.
Building Trust
When recipients see that you respect their privacy, they’re more likely to engage with your emails. Higher engagement rates (opens, clicks) signal to ISPs that your emails are wanted, improving your sender reputation.
Reducing Complaints
Privacy-conscious practices, like clear opt-in processes and easy unsubscribe options, lead to fewer spam complaints. Lower complaint rates are a key factor in maintaining a good sender reputation.
Cleaner Lists
By regularly updating consent and removing unengaged subscribers, you maintain a healthier email list. Sending to active, interested recipients improves your engagement rates and deliverability.
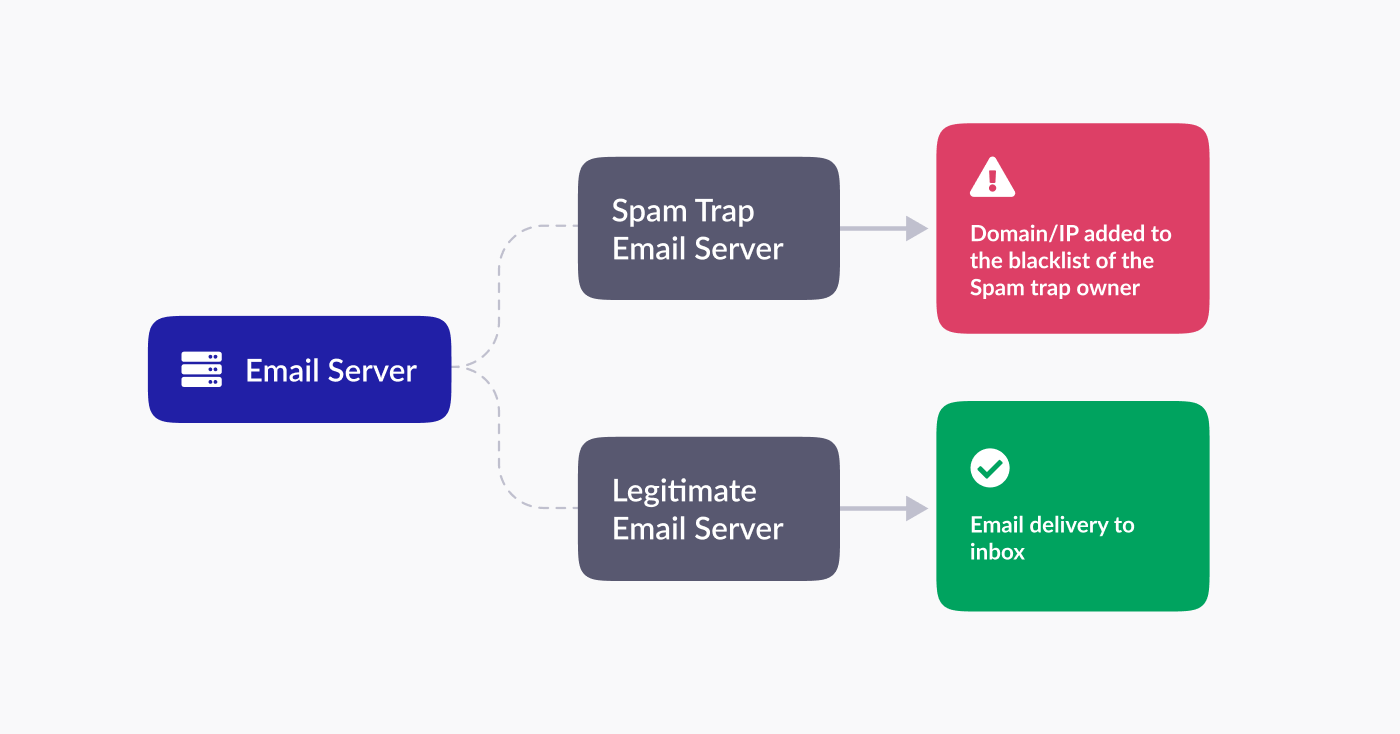
Avoiding Blocklists
Strict data privacy practices help you avoid accidentally emailing spam traps or people who haven’t given consent. This reduces your risk of being blocklisted, which can severely damage your deliverability.
Personalization Without Creepiness
Proper data handling allows you to personalize emails effectively without crossing privacy lines. This balance can lead to higher engagement without triggering privacy concerns.
Demonstrating Legitimacy
ISPs and email clients look favorably on senders who follow best practices, including privacy standards. This can result in better inbox placement.
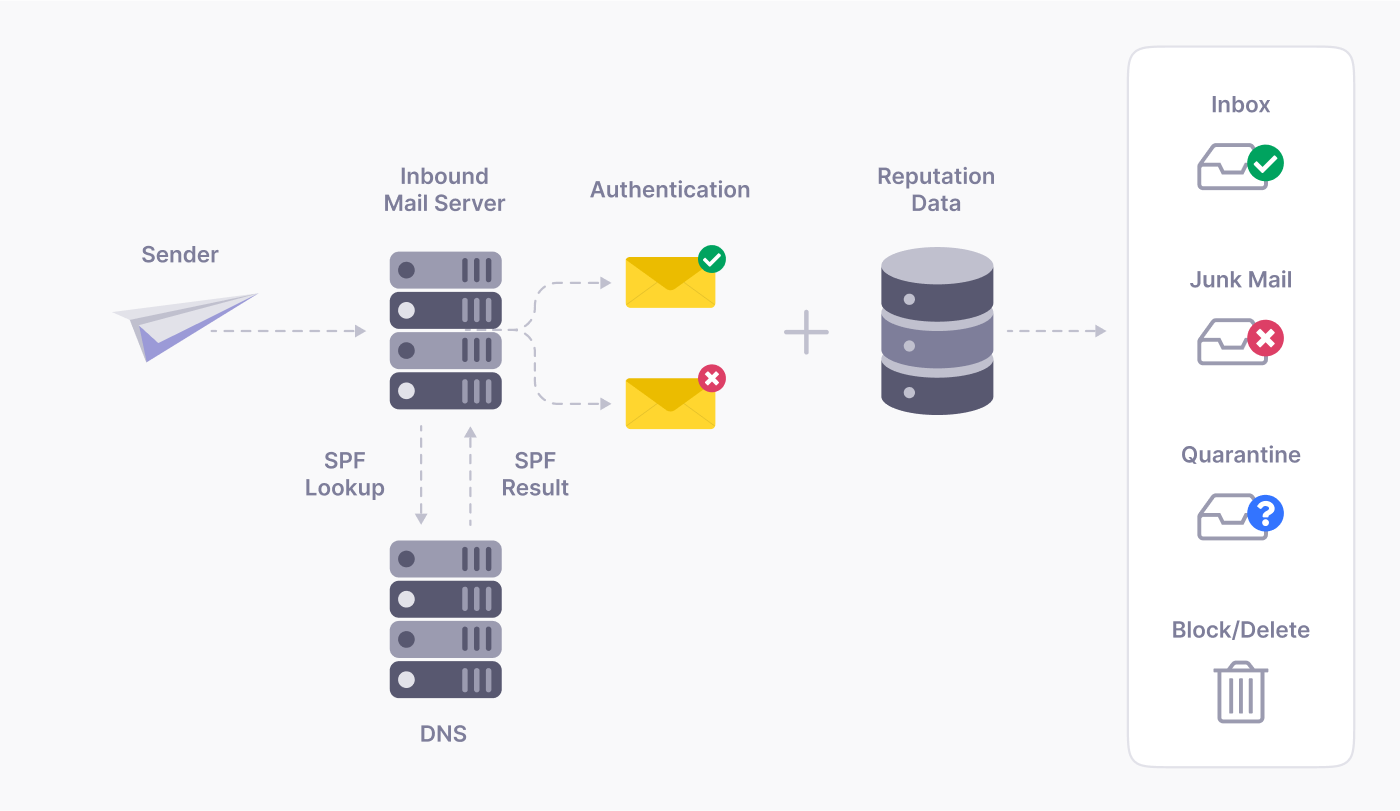
Additionally, many email authentication protocols (like DMARC) consider privacy practices. Implementing these can improve your deliverability and show ISPs you’re a trustworthy sender.
Avoiding Legal Issues
By staying compliant with privacy laws, you avoid potential legal problems that could harm your reputation and ability to send emails.
Key Privacy Regulations Impacting Transactional and Marketing Emails
Understanding how privacy regulations apply to both transactional and marketing emails is crucial for any business using email communications.
Here’s an overview of major regulations and their impact. Remember, while these points can help you to understand key aspects of email regulation and compliance, it’s always recommended to consult with legal professionals for specific advice.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)

The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a privacy law that came into effect in May 2018.
It applies to any organization that processes the personal data of EU residents, regardless of where the organization is located.
For email senders, the GDPR introduces strict requirements around consent, data processing, and transparency. It emphasizes the individual’s right to control their personal data, including how it’s collected, used, and shared.
This regulation has forced many organizations to overhaul their email practices, particularly in how they obtain and manage consent for marketing communications.
- Applies to all organizations processing personal data of EU residents
- Applies regardless of whether the processing takes place in the EU or not
- Requires explicit, affirmative consent (opt-in) for marketing communications
- Consent must be freely given, specific, informed, and unambiguous
- Pre-ticked boxes or silence do not constitute consent
- Must keep clear records of how and when consent was obtained
- Data subjects have the right to to access personal data and request erase of their data
CAN-SPAM Act

The CAN-SPAM Act is a law that sets the rules for commercial email in the United States. It was enacted in 2003 and applies to all commercial messages, which the law defines as “any electronic mail message the primary purpose of which is the commercial advertisement or promotion of a commercial product or service.”
The CAN-SPAM Act doesn’t require senders to get permission before sending marketing messages, making it less strict than GDPR in some aspects.
However, it does state that senders provide recipients with a clear way to opt out of future emails and promptly honor those requests.
- Applies to all commercial emails sent in the United States
- Prohibits false or misleading header information
- Requires that subject lines are not deceptive
- Requires the inclusion of the sender’s valid physical postal address
- Must provide a clear and conspicuous explanation of how the recipient can opt out of getting emails in the future
Canada’s Anti-Spam Legislation (CASL)
Canada’s Anti-Spam Legislation (CASL) is one of the strictest anti-spam laws in the world.
It came into effect on July 1, 2014, and applies to all electronic messages (including emails and texts) sent in connection with commercial activity.
CASL operates on an opt-in basis, meaning that in most cases, you need express consent before sending commercial electronic messages to recipients.
- Applies to commercial electronic messages sent to or from Canadian computer systems
- Requires express or implied consent before sending commercial electronic messages
- Requires that each message include a clear mechanism to unsubscribe
- Unsubscribe requests must be honored within 10 business days
- Imposes significant penalties for non-compliance, including penalties up to $10 million per violation
Best Practices for Maintaining Email Data Privacy
So what can you do to make sure you’re complying with all those regulations and don’t end up in legal trouble?
Data Collection
When it comes to data collection, transparency and consent are key.
Implement clear opt-in mechanisms that require active consent from your subscribers. This means using unchecked boxes and avoiding pre-ticked options that assume consent.
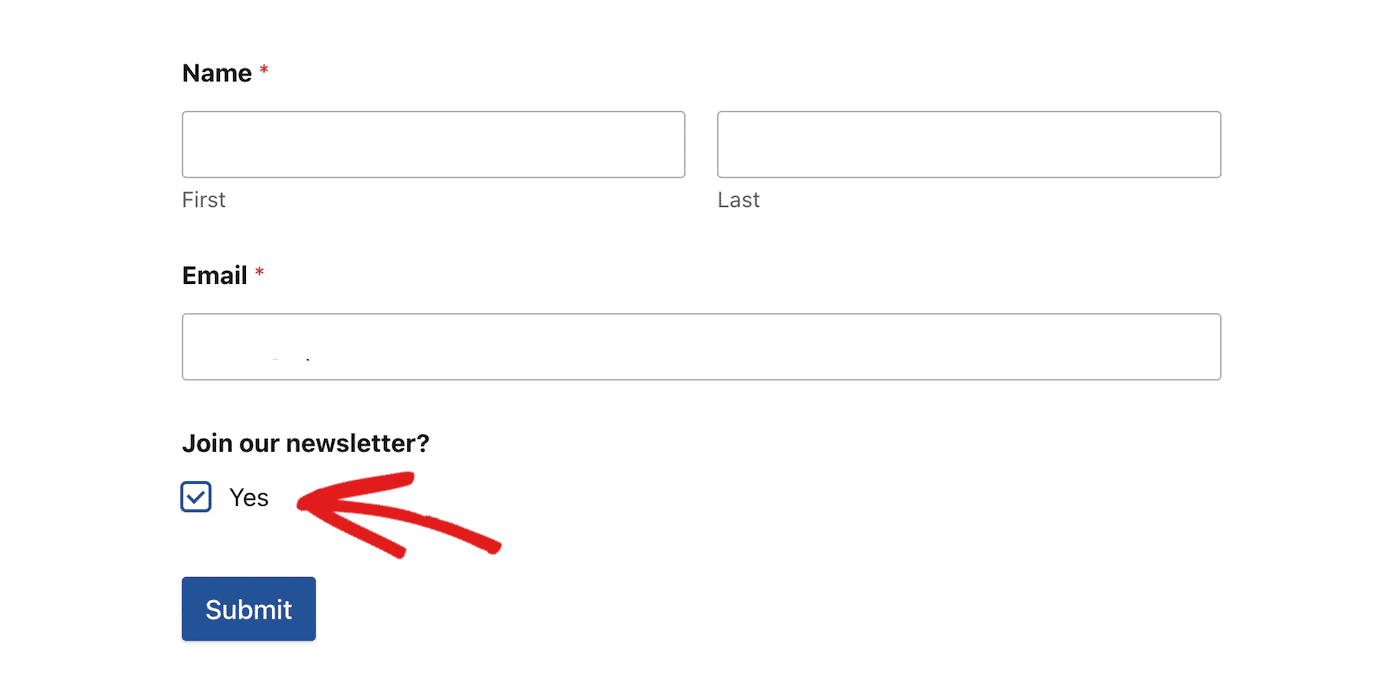
You should also consider using a double opt-in process for added verification, which is recommended by email providers such as Gmail.

Be upfront about how you plan to use the data you collect. Clearly state your intentions in simple, understandable terms, and make sure your privacy policy is easily accessible and regularly updated.
When designing data collection forms, keep them concise and only ask for necessary information.
And finally, remember to provide easy options for users to update their preferences or withdraw consent at any time.
Data Storage
Secure data storage is critical to maintaining privacy. Use reputable storage and email platforms with strong security measures, such as SendLayer, and implement multi-factor authentication for access to sensitive data.
Email encryption is crucial for protecting sensitive information both in transit and at rest. Use TLS for encrypting emails in transit. This helps prevent unauthorized interception of emails as they travel from your server to the recipient’s server.
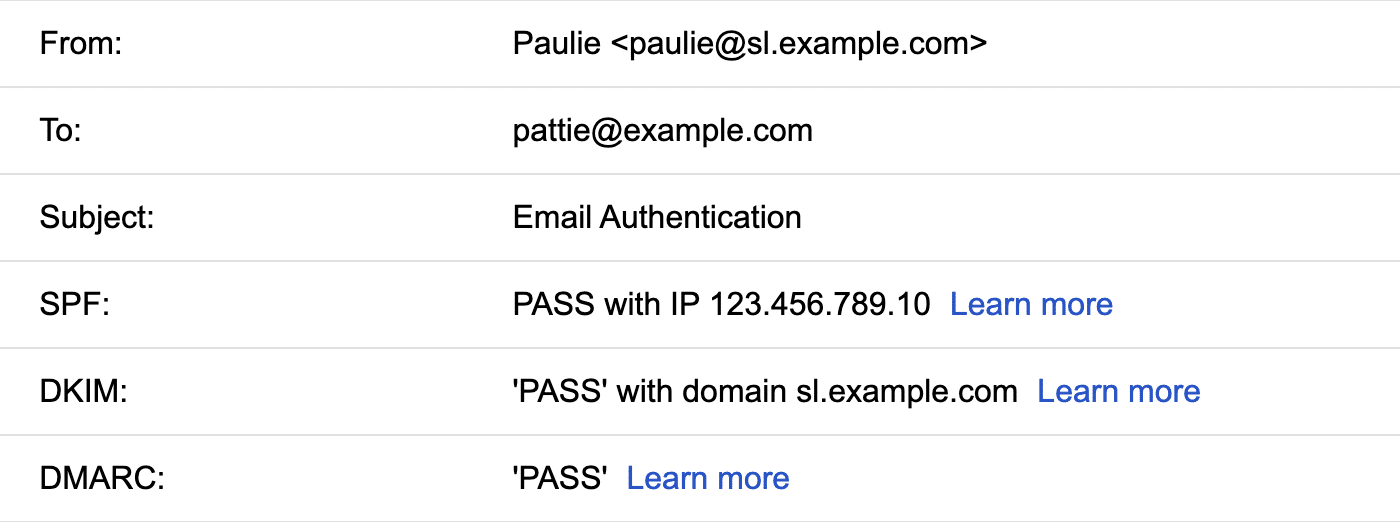
Authentication protocols are also vital to prevent email spoofing and phishing attempts. SPF, DKIM, and DMARC protocols work together to verify that emails are genuinely from your domain and haven’t been tampered with in transit.
Develop clear data retention policies specific to email data. This includes subscriber lists, email content, and engagement metrics.
Determine how long you need to keep different types of email data for business and legal purposes, and set up automated processes to delete or anonymize data that’s no longer needed.
AI and Email Data Privacy
As AI becomes increasingly integrated into email marketing and communication systems, it brings both opportunities and new privacy concerns.

It’s important to be aware of these issues and stay up to date with the latest developments to maintain trust with your subscribers and stay compliant with evolving regulations.
AI has made advanced personalization possible, along with predictive analytics and automated content generation.
But personalization algorithms may involve processing large amounts of personal data, including browsing history, purchase behavior, and engagement metrics. It’s crucial to make sure subscribers are aware of how their data is being used to personalize their experience.
When you’re using AI in your email processes, data protection should be a top priority. Only process the data necessary and never give subscriber or customer data to AI platforms that use your inputs to further train their models.
We’re likely to see new regulations around the use of AI and data privacy in the coming months and years so it’s wise to stay informed about emerging policies and up-to-date email marketing best practices.
That’s it! Now you know about email data privacy.
Next, do you need some inspiration for your email designs? Check out our roundup of the best welcome email examples for new customers.
