What Is CNAME?
A CNAME record maps one domain name to another domain name. It creates an alias to make it easy to point one to the other.
Unlike other types of DNS records, a CNAME record never points to an IP address. Instead, it can only point to another domain name.
What Do CNAME Records Do?
CNAME records apoint from one record to another.
For example, you might have an A record for your main domain that’s pointing to your server’s IP address. You can then add a CNAME record for any subdomains you want to create. Those would act like an alias; they simply point to the A record.
If you switch hosting providers and your IP address changes, you only need to change the A record. The CNAME records would all pick up that change without you having to edit them.
How Are CNAME Records Resolved?
In this example, we’ll explain what happens if your main domain is sendlayer.com, and you have a CNAME set up for a subdomain of www. This is how your browser would locate www.sendlayer.com and display the site:
Local Resolver Check
The client’s browser checks a server called a DNS resolver for the address www.sendlayer.com.
Authoritative Nameserver Check
The DNS resolver finds the authoritative nameserver that has the address information for www.sendlayer.com.
CNAME Resolved
The authoritative nameserver resolves the DNS request and returns the CNAME record to your computer.
Local Resolver
Your computer now knows that www.sendlayer.com is an alias for sendlayer.com.
It sends a new request to obtain the IP address for sendlayer.com.
Authoritative Resolver
The process repeats but this time, the authoritative nameserver returns the actual IP address for sendlayer.com.
Local Resolver
Your computer locates the server associated with sendlayer.com and displays the website.
How Are CNAME Records Used in SendLayer?
We use a CNAME record when you first verify your domain with us. It acts as an alias – just as we explained in the example above.
When you add your domain, you’ll create a CNAME for each of these DNS records:
Once those records have been created, we’ll handle any changes or updates on our side. So you don’t need to change your DNS records again if something needs to be updated in the future.
What Does CNAME Proxy Mean?
If you manage your DNS records with a provider like Cloudflare, it will automatically proxy CNAME records when you add them. That means Cloudflare will attempt to cache requests for those records.
The proxy status is shown with an orange cloud when you add your DNS records for SendLayer.
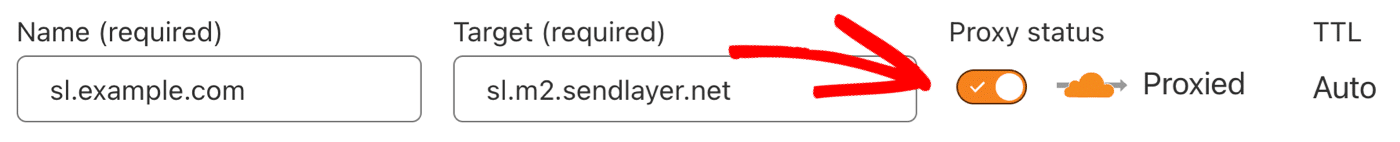
To make sure that SendLayer can verify your DNS records, we recommend that you turn off the proxy for the CNAME records you add.
You can do this by clicking the toggle switch next to the cloud icon.
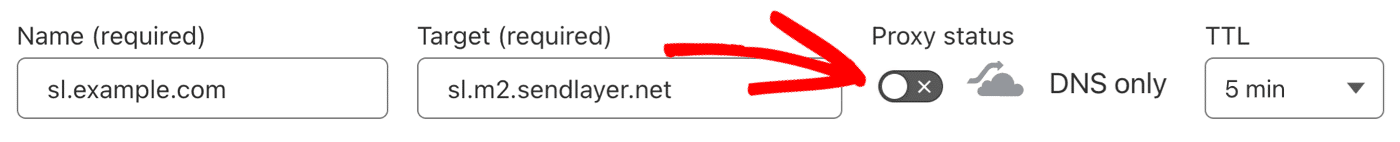
Turning proxying off in Cloudflare also allows you to set the TTL to 1 day, which is our recommended setting.
That’s it! Now you know how CNAME records work.
Next, would you like to learn how to set up your CNAME records for SendLayer? Check out the following resources: