What Is DMARC?
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) is an email authentication protocol.
It is used to verify the sender’s identity and prevent such issues as spam and email spoofing. DMARC implements 3 main policies:
- None
- Quarantine
- Reject
The DMARC protocol depends upon the SPF and DKIM protocols, and at least one of these must be present for it to work.
DMARC records are stored in the DNS (Domain Name System) as CNAME records and do not point to an address.
What Do DMARC Records Do?
The DMARC record specifies what to do if an authentication failure occurs for emails sent from your domain. For example, the information in the DMARC record helps the recipient server decide whether to mark a suspicious email as spam or even reject it.
For any mail sent from your domain, the DMARC record also plays a role in verifying the from email address. Overall, the primary role of the DMARC protocol is to protect your domain from unauthorized use.
How Are DMARC Records Used in SendLayer?
When you add a domain to your SendLayer account, a corresponding DMARC record is generated automatically.
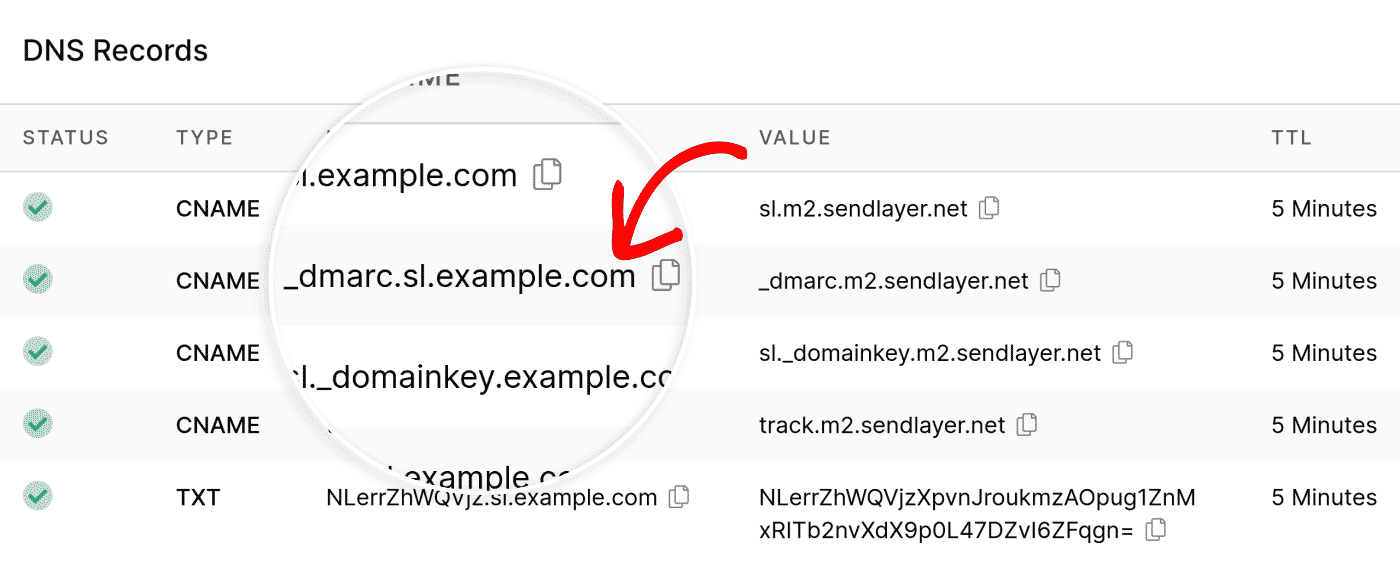
This record is used to help protect your domain from unauthorized usage.
That’s it! Now you know how DMARC records work.
If you’d like to learn how to set up your DMARC records for SendLayer, check out the following articles: