Are you wondering why SendLayer sends email from a subdomain?
When you set up a new account with SendLayer, the platform automatically creates a subdomain to send your email from. If your domain is example.com, SendLayer will send your email from sl.example.com.
It’s important to send certain types of emails from a subdomain if you want to ensure deliverability and protect your sender reputation. In this article, we’ll explain what an email subdomain is, and when you should use one.
What Is a Subdomain?
A subdomain is the prefix or portion of text that comes before the “main” root domain. If the main domain is example.com, www.example.com would be one possible subdomain. A single domain can have hundreds of subdomains, each serving a different purpose.
But let’s back up a little and recap what a domain name is.
A domain name is an easy-to-remember text identifier that you can use to access a website. You can access any website by typing the IP address of the server that hosts it into your browser. But it’s not easy for most people to remember long strings of numbers. Instead, a user can type a domain like sendlayer.com into their browser.
The browser uses a service called the Domain Name System (DNS) to look up the IP address linked to the domain name. This is similar to how you might look up a friend’s telephone number by searching for their name in your phone contacts.
Common Uses for Different Subdomains
Subdomains are commonly used in websites to create separate sections from the main site or even completely separate websites with a unique design, layout, and navigation.
For example, you might use subdomain names like store.example.com for your online store or blog.example.com for your blog. Popular hosted blogging services like WordPress.com use subdomains to give each user a different web address like mywebsite.wordpress.com.
Some of the most common reasons for setting up a subdomain include:
- Create individual sections of your website for an online store, support hub, blog, or other purposes
- Publish more websites without the need to buy different domains
- Duplicate your main website in another language
- Give multiple users their own sites under the umbrella of your domain
- Create a testing or staging version of your website
- Create a mobile version of your site
But subdomains aren’t only for websites. You can also use subdomains for other purposes, including sending email. If you have a look in your inbox, you’ll probably see several email subdomain examples, such as [email protected].
How Subdomains work
Subdomains have their own entries in the DNS. This means they can point at different IP addresses and refer to completely different websites or web properties.
Going back to our phone number analogy, several companies could be located in a single building (domain), but they’d each have their own office and telephone number.
Internet service providers (ISPs) treat subdomains as separate websites. This can make things tricky for things like SEO, but it also offers advantages, especially when it comes to sending emails.
As well as specifying the IP address a website is hosted at, there are DNS records that include information for routing email. You can add a DNS record to instruct your outgoing emails to be sent from a subdomain.
These records hold data on the mail servers that are used for sending and receiving email and can also be used to authenticate emails to prevent unauthorized use of your email domain.
Just as website subdomains are treated separately from the main site, using email subdomains keeps your email separate from your website in terms of email reputation.
You can find out more about email authentication and different types of DNS records at our guides on:
Why Send Email From a Subdomain?
When you set up a separate subdomain for your email and only send email from that subdomain, it separates your email from your website and other online properties.
This comes in very useful if your domain is ever blacklisted or flagged for sending spam.
Let’s say you send your email from example.com without setting up a new subdomain.
If a lot of recipients mark your emails as spam in their email clients, this puts your domain (example.com) at risk.

Email service providers keep track of domains that send emails frequently marked as spam and may put them on a blacklist to protect their users.
However, if you’d set up a subdomain such as mail.example.com and sent all your email from this subdomain, only the subdomain and not your main domain would be blacklisted.
Your main domain’s reputation would stay protected, and you could set up another subdomain for sending emails without issue.
Of course, it goes without saying that you should never set up a subdomain for the purpose of sending spam emails. But email providers like Gmail and Yahoo can often blacklist emails due to an innocent mistake or poor email practices. Some of the most common reasons for being blacklisted include:
- Poor email hygiene: Not keeping your mailing list up to date and sending emails to inactive subscribers
- High email bounce rate: Sending emails to invalid email addresses
- Too many spam complaints: Sending too many sales-focused emails or words that trigger spam filters
When you add a domain to SendLayer, the platform automatically creates a subdomain, such as sl.example.com, which protects the reputation of your main domain.
If you inadvertently end up on a blacklist or there’s some other problem with your email subdomain, you can change to a new one without affecting your website and other online properties.
When to Use an Email Subdomain
You don’t need to use a subdomain or SendLayer to send all your emails. You can send regular personal and business emails from your parent domain, and you shouldn’t have any issues.
But there are some different types of emails where we recommend using a different subdomain:
- Promotional email: If you’re sending email marketing messages to a list, there’s a high chance of some of them being marked as spam. So it’s highly advisable to set up a subdomain for your sales messages and marketing email campaigns. If you send a high volume of email, you may even want to consider setting up multiple email subdomains for different audiences.
- Outreach emails: Likewise, if you’re sending outreach emails for PR purposes, to look for guest posting opportunities or partnership requests, these emails have lower engagement rates and are more likely to be marked as spam. So it’s a good idea to create a subdomain for your outreach and PR emails.
- Transactional emails: It’s crucial that emails sent directly from your website, such as order confirmations, account notifications, password resets, and so on, reach the recipient and don’t end up in the spam folder. It makes sense to use a subdomain for these emails to improve deliverability and reduce the risk of your email being inadvertently blacklisted.
Using subdomain email addresses is also helpful for marketing, as it makes it easier to track the deliverability of different types of emails. Transactional emails almost always have higher engagement rates than marketing campaigns, for example, so it makes sense to measure the metrics of these emails separately.
Luckily, it’s pretty easy to set up a subdomain for your transactional email by using SendLayer.
How to Send Email From a Subdomain
The easiest way to set up a subdomain to send transactional emails from is by using SendLayer. SendLayer will automatically set up a subdomain for your email and also has features like trackable unsubscribe links and suppression lists to reduce email deliverability issues and keep your domain off blacklists.
1. Create a SendLayer Account
You can get started with SendLayer by visiting the pricing page and choosing the plan that’s most suitable for the volume of emails you’ll be sending. If you want to try out the service before signing up for a plan, click on the free trial link at the bottom of the pricing table.
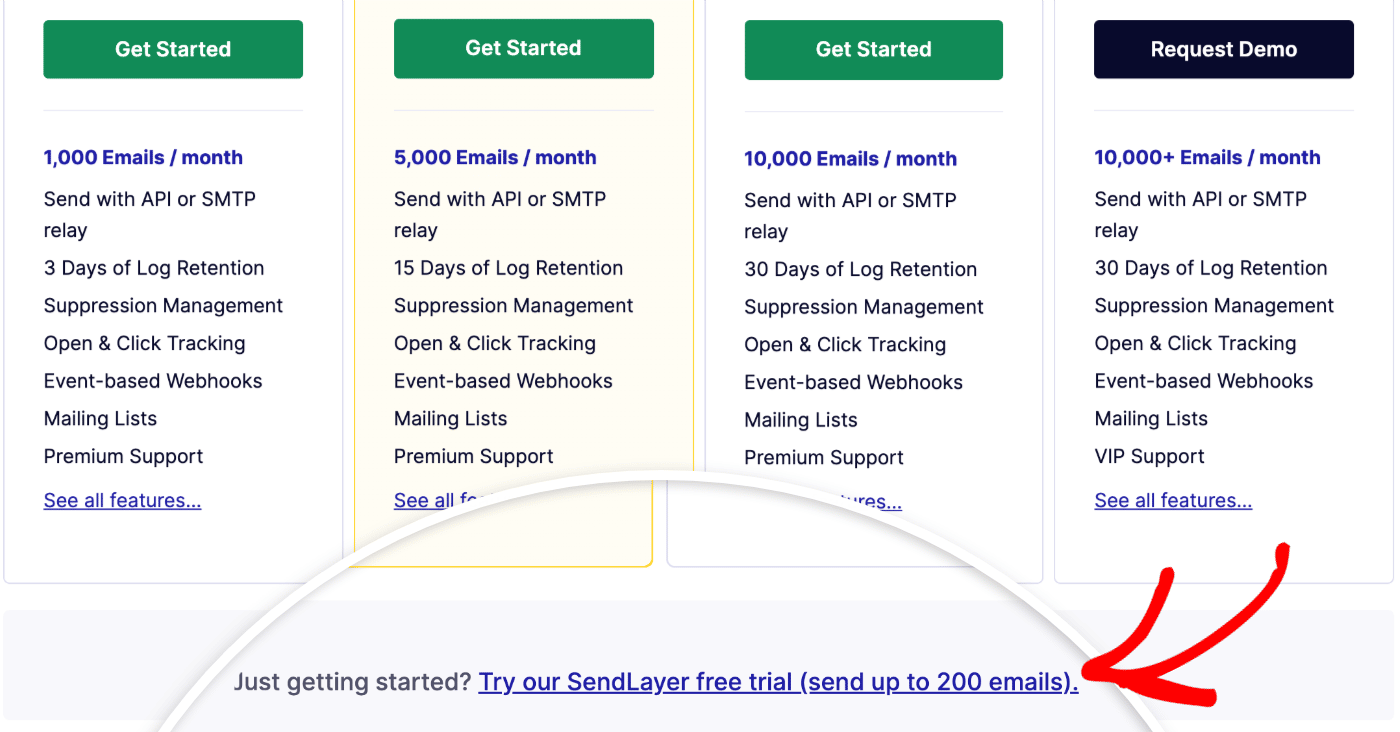
Continue to fill out your payment details and check out to create your account.
2. Add Your Domain
After creating your SendLayer account, log into your dashboard and click the Add Domain button.
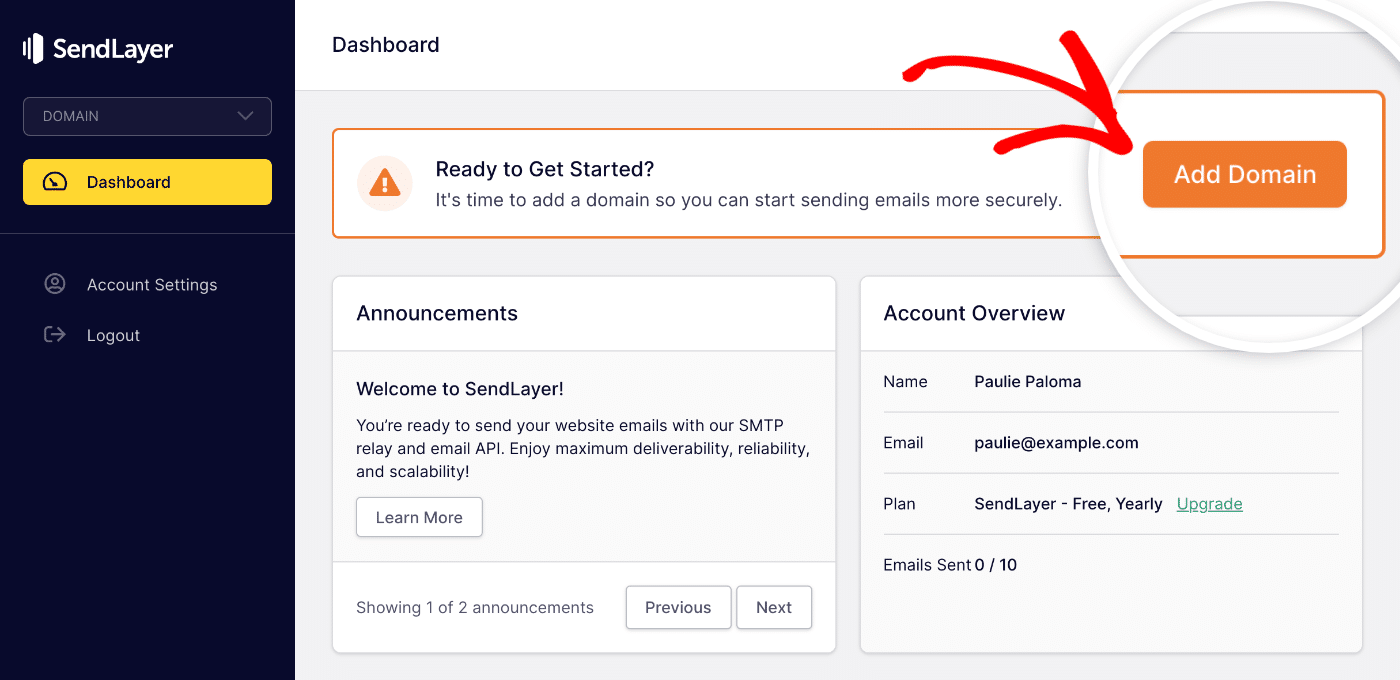
Enter your domain in the form that appears next, and click the Add Domain button.

SendLayer will create five new DNS records for your domain. You’ll notice that they all contain “sl.” This is the subdomain SendLayer automatically sets up for your email.
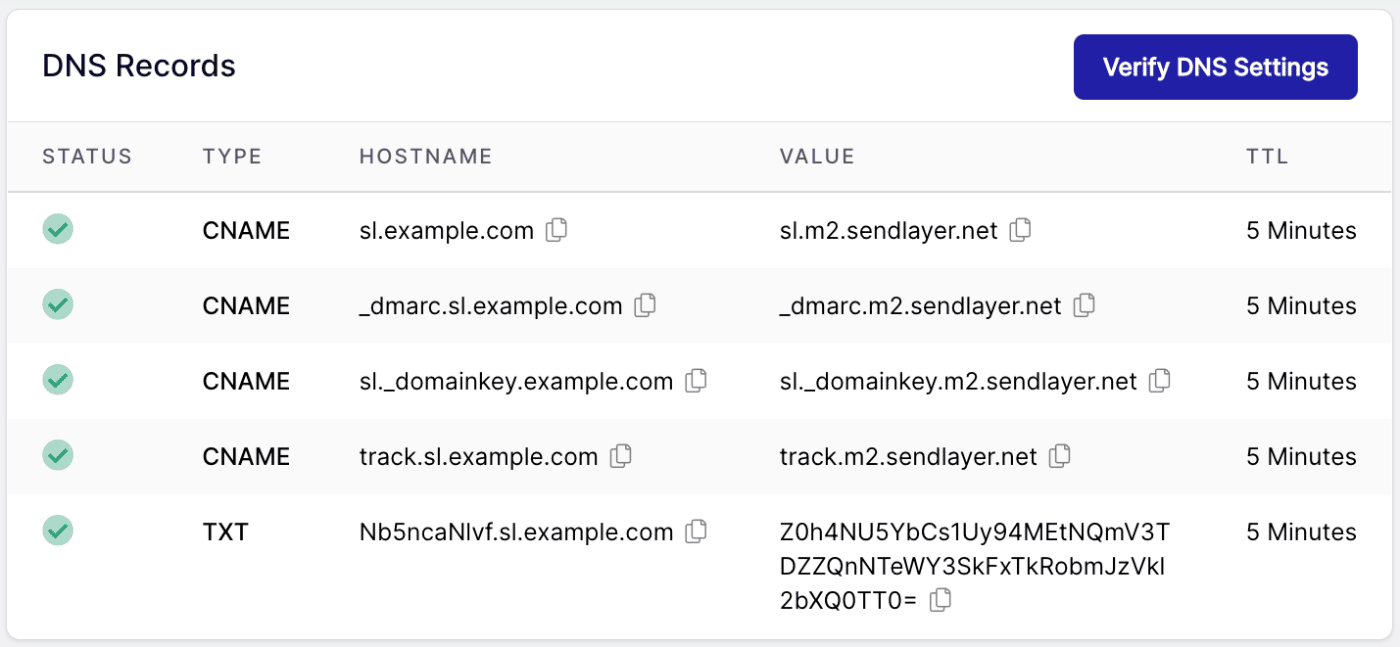
3. Add DNS Records to Your Web Hosting Account
You’ll need to copy each one of these DNS records by clicking the clipboard icons and manually add them to your DNS records in your web host settings.
Where to find these settings varies depending on your web host. You can see full instructions and specific guides for popular hosts in our guide to completing domain setup.
When you’ve added all the DNS records, scroll down and confirm by checking the I have added these DNS records and am ready to proceed checkbox. Click the Verify DNS Records button to complete verification.
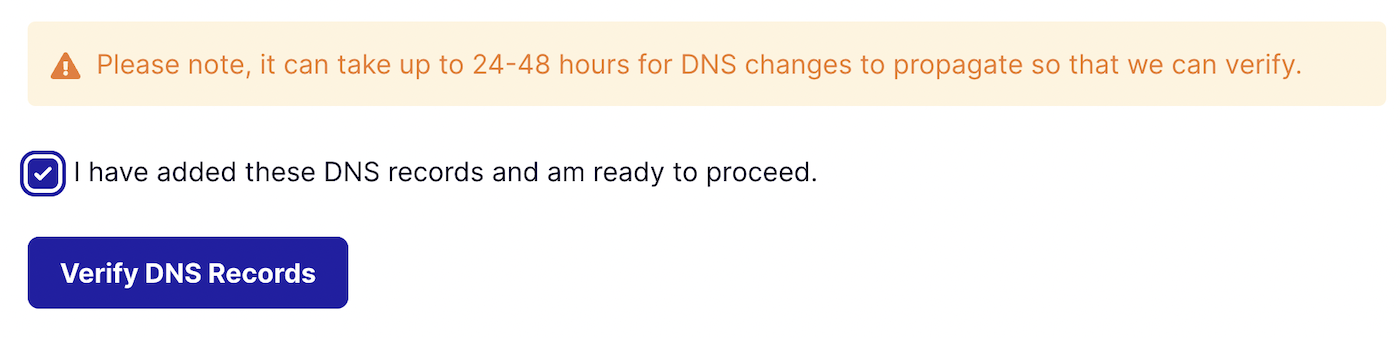
Once you’ve added your DNS records, you may have to wait a while until they’re fully propagated. For many hosts, this process takes just a few minutes, but it can sometimes take 24 hours or more for DNS changes to take effect.
You’ll know your DNS records have been updated successfully when there’s a green checkmark next to each record.
4. Connect Your Site or App With SendLayer
Now your SendLayer account is all set up and ready to use. There are two ways to connect your website or application to SendLayer: API or SMTP. You can read our documentation on integrating with SendLayer for an explanation of the two methods and more information to help you choose.
As an example, let’s go through the process of connecting your WordPress website to SendLayer to send transactional emails.
First, you’ll need an SMTP plugin. We recommend Easy WP SMTP as it’s easy to set up and integrates seamlessly with SendLayer. It’s quick and easy to connect Easy WP SMTP to SendLayer via API.
After you purchase the plugin, you can download it and find your license key in your dashboard. Make sure to enter your license key in the plugin settings before you can use it. If you need any help during installation, there are full steps in this guide.
Once you’ve installed and activated Easy WP SMTP, you need to configure it to use SendLayer. In your WordPress dashboard, navigate to Easy WP SMTP » Settings and scroll down to the Mailer settings. Choose Sendlayer as your mailer.

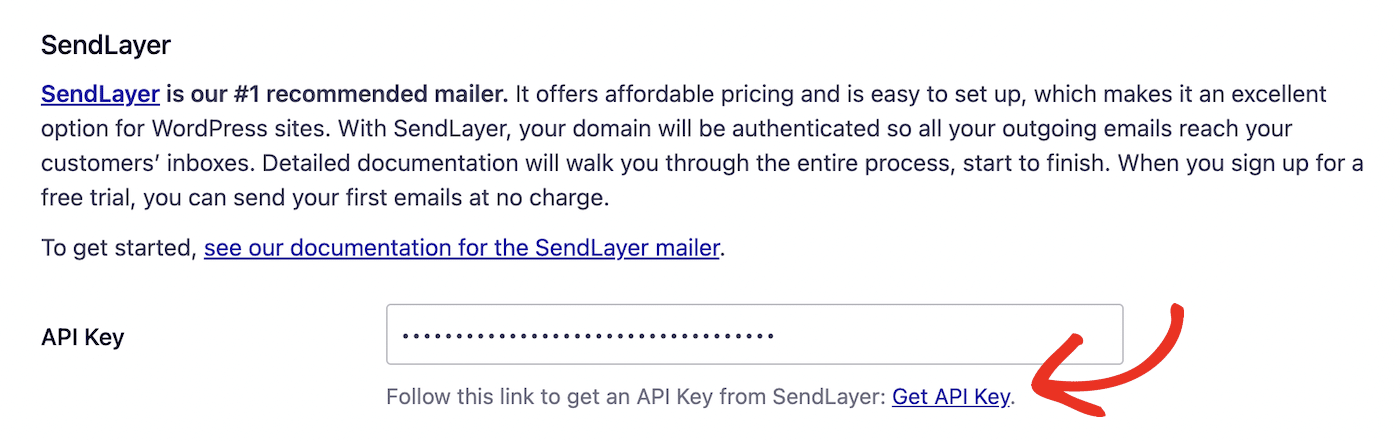
scroll down and paste in your SendLayer API key. You can use the provided link to Get API Key to go right to your SendLayer dashboard.
Now enter the rest of your email settings.
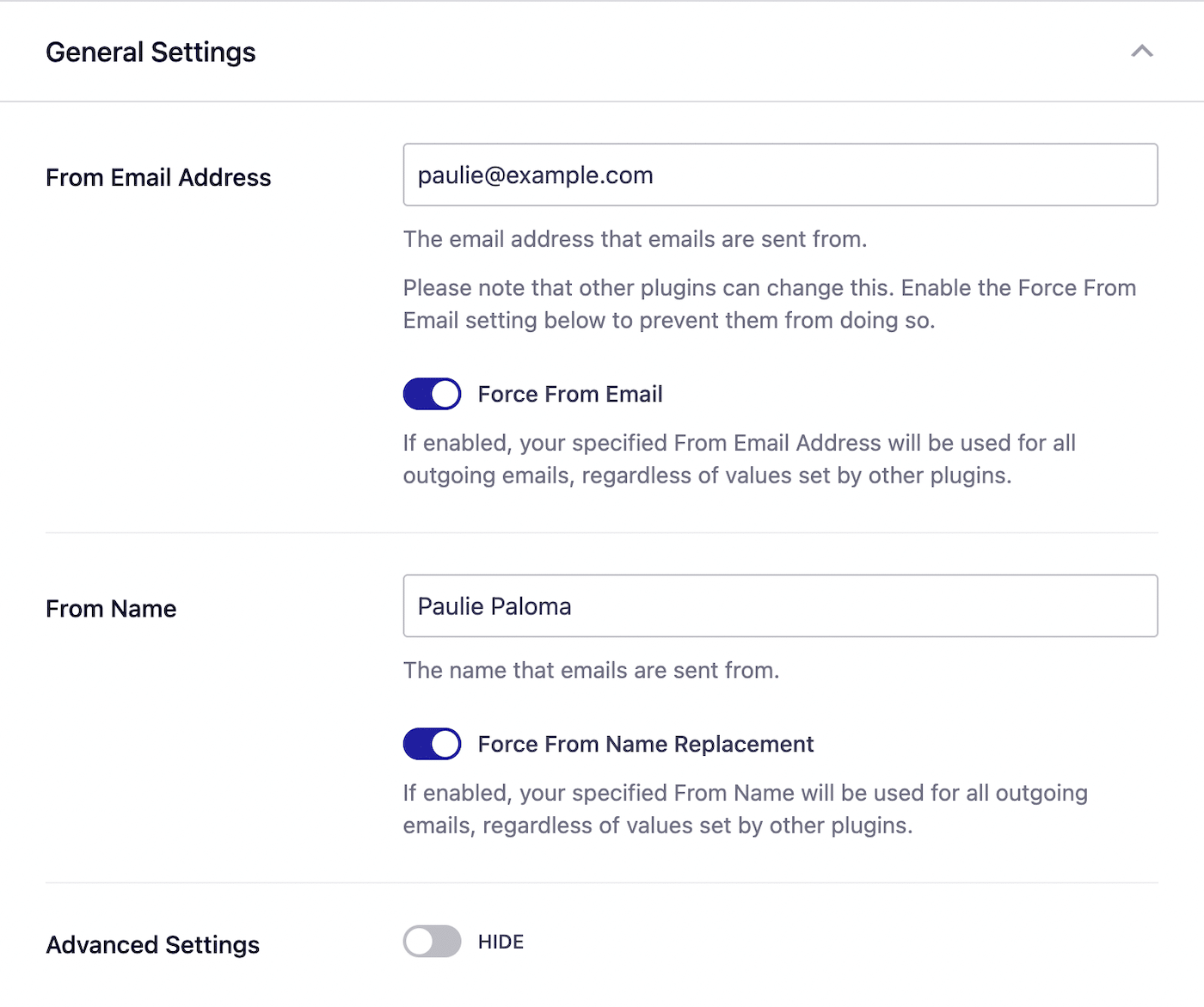
- From Email Address: This email should use the same domain you authorized with SendLayer
- Force From Email: We recommend enabling this option so that the From Email you set here will be used by all plugins on your site.
- From Name: The name you want to appear as the sender of emails sent from your site. By default, this is your site name, but you can change it to anything you choose.
- Force From Name Replacement: Again, if you enable this option, the email sender name you entered will be used by all plugins that send emails from your site.
And that’s it! You’ve now set up Easy WP SMTP to use SendLayer to send your emails from a subdomain.
To make sure it works, you can go to Easy WP SMTP » Send a Test, enter your email, and click the Send Test Email button. You should receive an email like the one below:
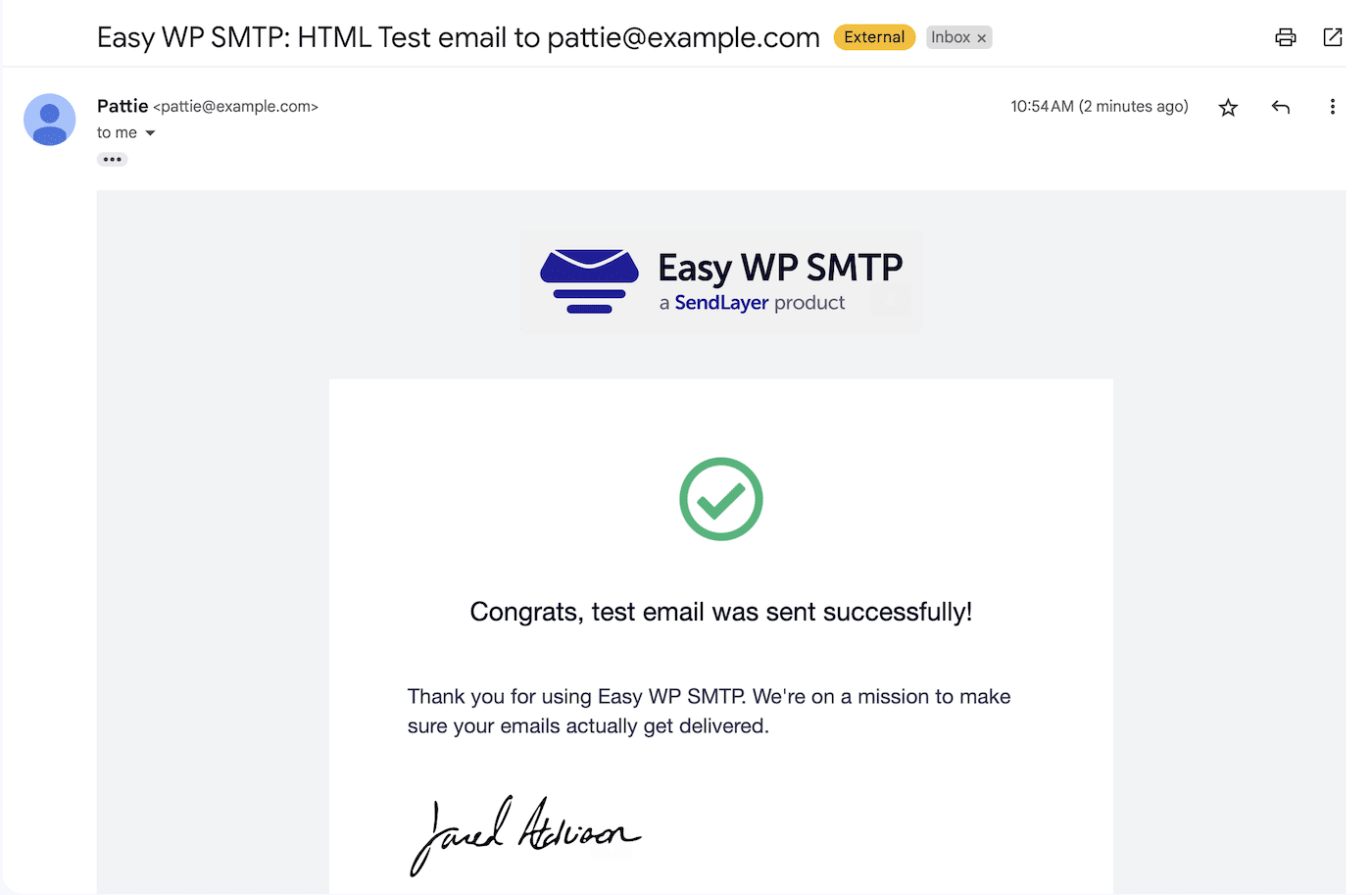
It worked! You can now rest easy in the knowledge that your transactional emails are being sent safely from a subdomain, improving deliverability and protecting the reputation of your main domain.
That’s it! Now you know why you should send email from a subdomain.
Next, would you like to learn more about transactional email? Check out our beginner’s guide to transactional email for more information.
Ready to send your emails in the fastest and most reliable way? Get started today with the most user-friendly and powerful SMTP email delivery service. SendLayer Business includes 5,000 emails a month with unlimited mailing lists and premium support.
